Telemedicine Improves Epilepsy Care Access and Satisfaction
Researchers studied how telemedicine can help people with epilepsy by looking at various studies on its use for diagnosis and management.

Researchers studied how telemedicine can help people with epilepsy by looking at various studies on its use for diagnosis and management.
This study looked at how a medication called dexmedetomidine affects brain activity readings during epilepsy surgery.

Researchers studied a 5-year-old girl with a severe form of epilepsy called drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) caused by a condition known as hemimegalencephaly, where one side of the brain is abnormally large.

Researchers studied the potential risks of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) in children whose fathers used valproate, a medication often prescribed for epilepsy, during the time they were producing sperm.

This study looked at how an educational program based on the Information-Motivation-Behavior Skills (IMB) model could help adolescents with epilepsy manage their condition better.

Researchers studied the potential risks of neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) in children whose fathers used a medication called valproate during the time they were producing sperm.

Researchers studied children with septo-optic dysplasia (SOD), a condition that affects vision and brain development, to understand what factors might lead to seizures in these patients.

Researchers studied how brain activity patterns might predict whether children with drug-resistant focal epilepsy would benefit from vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), a treatment option for epilepsy.
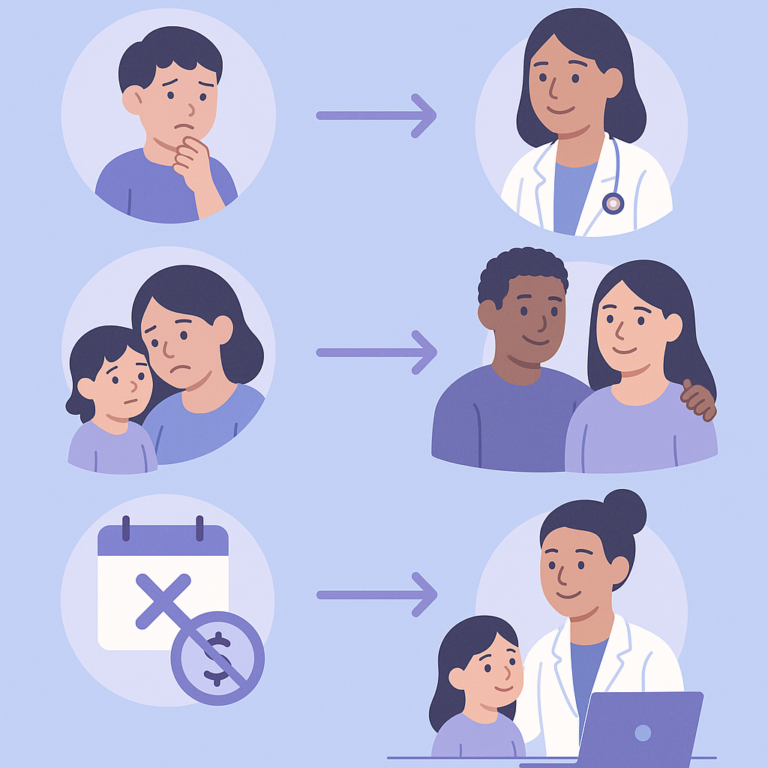
This study looked at the reasons why children with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) often experience delays in getting surgery that could help them.