Understanding a New Surgical Technique for Brain Surgery
Summary
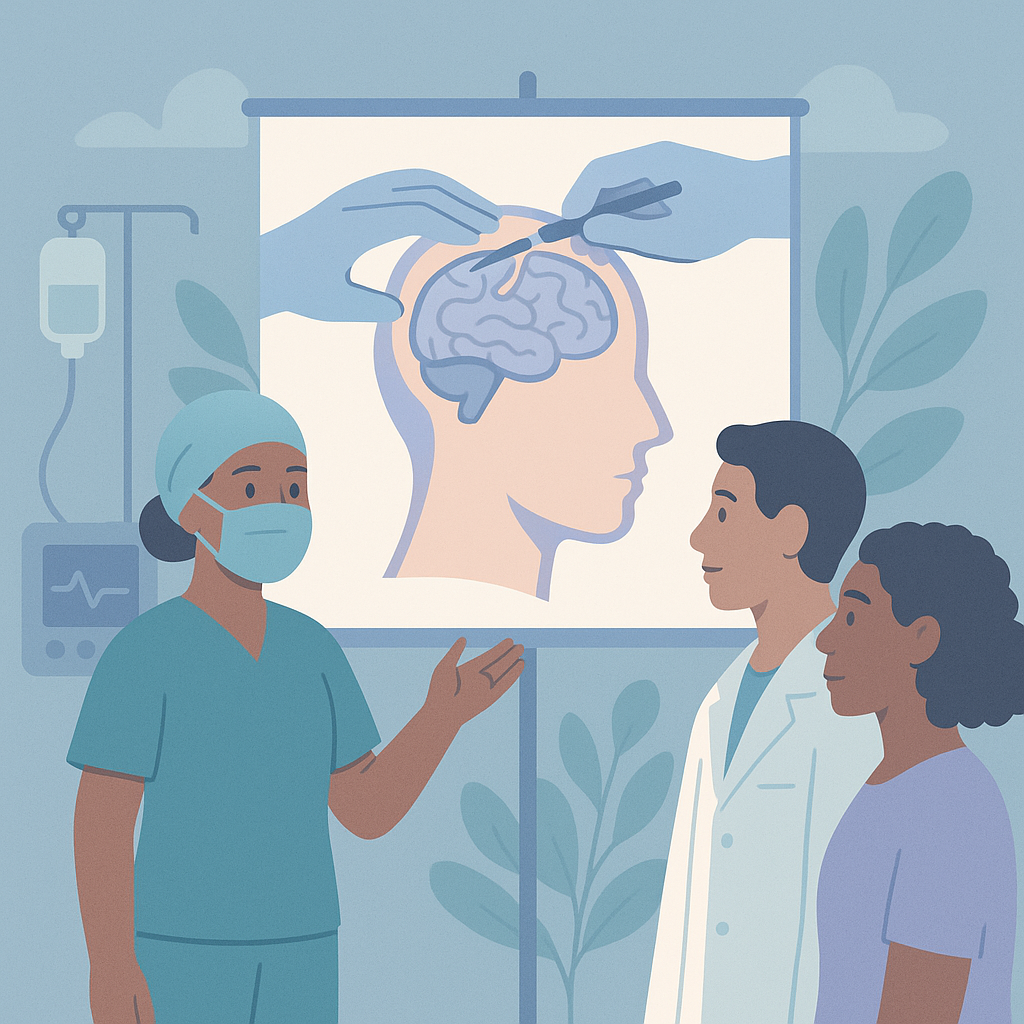
Researchers examined a surgical technique called vascular-guided transsylvian hemispherotomy, which is used to treat severe epilepsy. The study involved a group of patients who underwent this procedure, focusing on the anatomy of the brain, particularly the peri-insular sulci, which are grooves on the surface of the brain near the insula. The goal was to understand how this surgical approach can be improved by considering the brain's vascular structures.
The main finding of the study suggests that taking into account the specific brain anatomy and blood vessels can help surgeons perform the procedure more effectively. By using this method, the researchers believe that it may lead to better outcomes for patients with epilepsy, including potentially reducing the frequency of seizures. However, the exact impact on seizure control and recovery was not quantified in this summary.
This research is important because it could enhance surgical techniques for treating epilepsy, offering hope for patients who do not respond to medication. However, it is essential to note that the study may have limitations, such as a small number of patients and being observational in nature. More extensive studies are needed to confirm these findings and understand their long-term effects.
Related reading
- New Model Predicts Dementia and Death Risk in Older Veterans
- New Diazepam Film Offers Hope for Kids with Epilepsy
- Boosting Self-Efficacy Can Improve Life for Kids with Epilepsy
- Neurologists Generate More Revenue Than Nonneurologists After Patient Visits
- Correction on Neurostimulation Study for Epilepsy and Tourette Syndrome
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation May Help Treat Immune Diseases
Free: Seizure First Aid Quick Guide (PDF)
Plus one plain-language weekly digest of new epilepsy research.
Unsubscribe anytime. No medical advice.