Comparing Laser Therapy and Surgery for Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
Source: Journal of neurosurgery
Summary
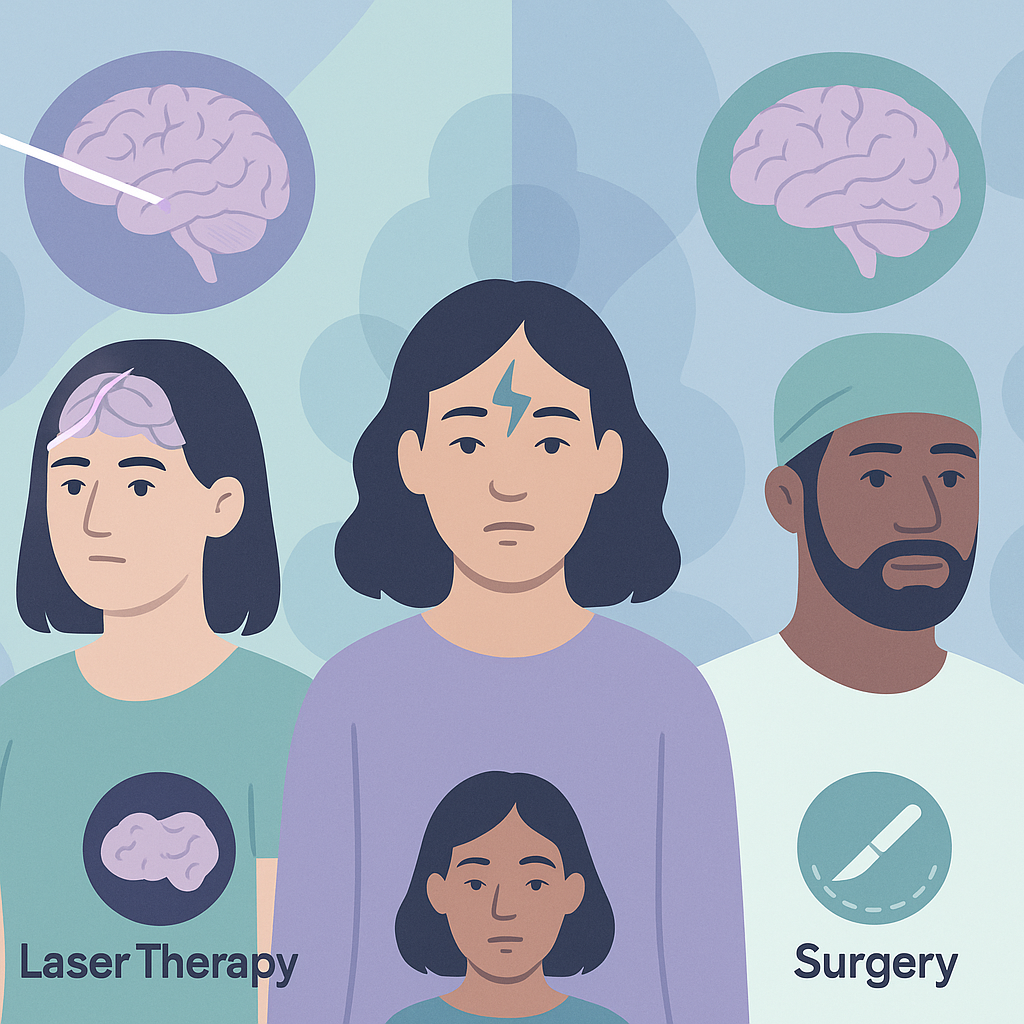
Researchers studied two surgical treatments for people with drug-resistant epilepsy: open resective surgery (ORS) and laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT). They looked at data from 15 studies involving a total of 3,873 patients to compare how well each treatment worked in reducing seizures, how long patients stayed in the hospital, and the rates of complications after surgery.
The findings showed that ORS had a higher success rate in achieving seizure freedom, with 67.1% of patients becoming seizure-free compared to 52.5% for LITT. However, LITT patients had shorter hospital stays and fewer complications, including a lower risk of serious issues like strokes and permanent neurological problems. When looking at matched studies, the difference in seizure freedom rates between the two treatments was not significant, especially for patients with temporal lobe epilepsy.
This research is important because it helps doctors and families understand the trade-offs between these two surgical options. While ORS may lead to better seizure control, LITT offers a safer and less invasive alternative with fewer complications. However, the study has limitations, such as the need for more research to match patient groups and evaluate long-term outcomes like quality of life.
Free: Seizure First Aid Quick Guide (PDF)
Plus one plain-language weekly digest of new epilepsy research.
Unsubscribe anytime. No medical advice.