SEEG Improves Epilepsy Surgery Outcomes with Expert Care
Source: Neurosurgical review
Summary
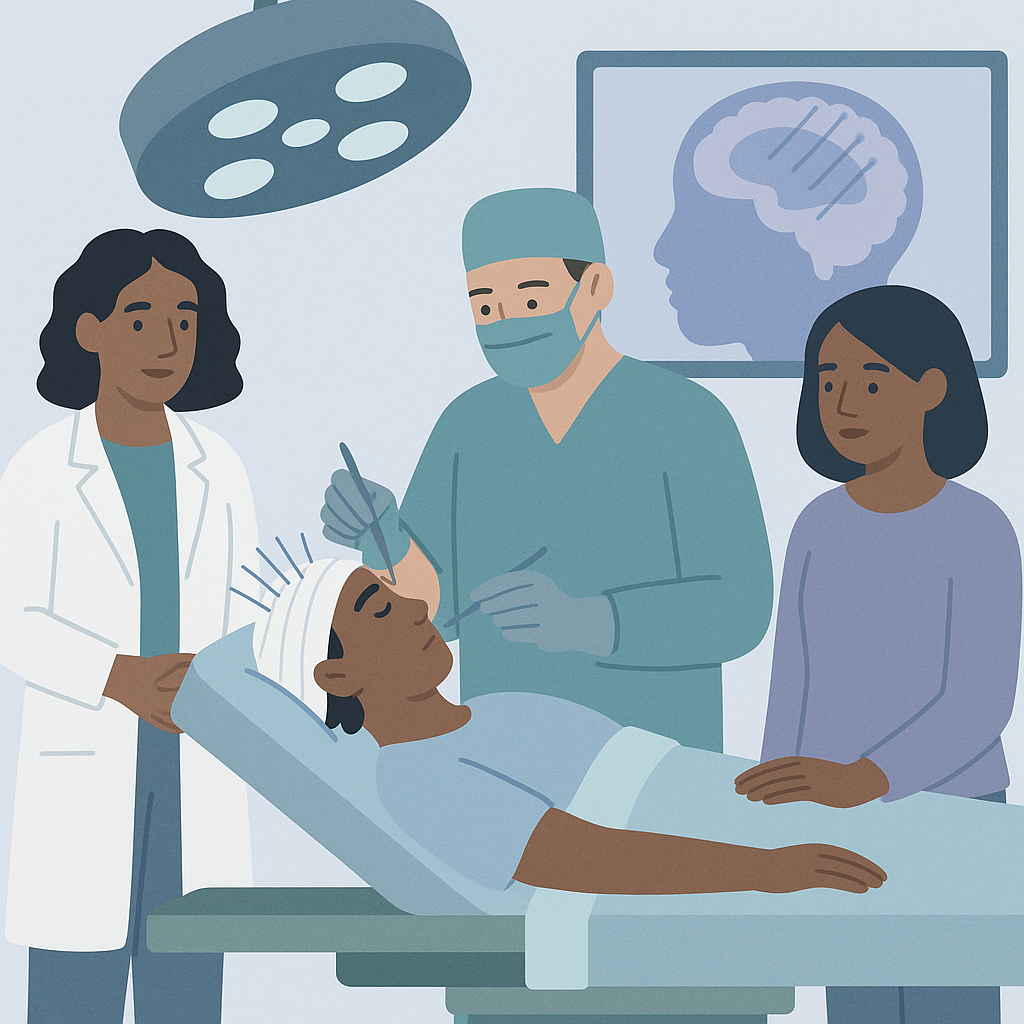
Researchers studied the use of stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) in patients with drug-resistant focal epilepsy. They reviewed 50 studies that included over 6,000 patients, focusing on how well SEEG works for diagnosing epilepsy and the outcomes of treatments that follow. The studies were mostly from high-income countries and looked at various factors that might affect the success and safety of SEEG procedures.
The findings showed that SEEG is generally very effective in identifying the areas of the brain causing seizures, with many studies reporting high success rates. However, there were also complications, mainly intracranial hemorrhages, with fewer complications seen in hospitals that perform a lot of these procedures and use advanced technology. After SEEG, many patients underwent surgery, and a significant number achieved a favorable outcome, meaning their seizures were greatly reduced or eliminated.
This research is important because it highlights how the success of SEEG can depend on the experience of the medical team and the resources available at the hospital. While SEEG is a valuable tool for treating epilepsy, there are still challenges, especially in less-resourced areas. Improving training and access to this technology can help ensure that more patients receive the best possible care.
Free: Seizure First Aid Quick Guide (PDF)
Plus one plain-language weekly digest of new epilepsy research.
Unsubscribe anytime. No medical advice.