New Genetic Variants Found in Epilepsy Among Pashtun Families
This study focused on families from the Pashtun population in Pakistan who have cases of epilepsy that had not been thoroughly examined at the genetic level.
This hub covers epilepsy EEG and MRI: how EEGs and brain imaging help doctors understand seizure patterns and possible causes. Clear explanations of common findings and what research suggests.
Yes. EEGs are a snapshot. Some people need repeat EEGs, sleep-deprived EEGs, or long-term monitoring.
Not always. It raises suspicion and risk, but diagnosis still depends on the full story.
To look for structural causes like scars, malformations, tumors, and stroke-related changes, which can guide treatment.
An inpatient or extended study that records EEG and video together to match symptoms to brain activity.
This study focused on families from the Pashtun population in Pakistan who have cases of epilepsy that had not been thoroughly examined at the genetic level.
Researchers studied how to find and confirm specific microRNA markers in blood plasma that could help predict post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE) after brain injuries.

This study looked at how EEG (electroencephalography) readings can help identify different types of genetic epilepsy in children and how these readings relate to their neurological outcomes.
Researchers studied the use of two types of brain monitoring—scalp EEG (scEEG) and stereo EEG (SEEG)—in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy.
Researchers studied six Chinese children diagnosed with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy (PDE) to understand the clinical features and genetic changes related to this condition.
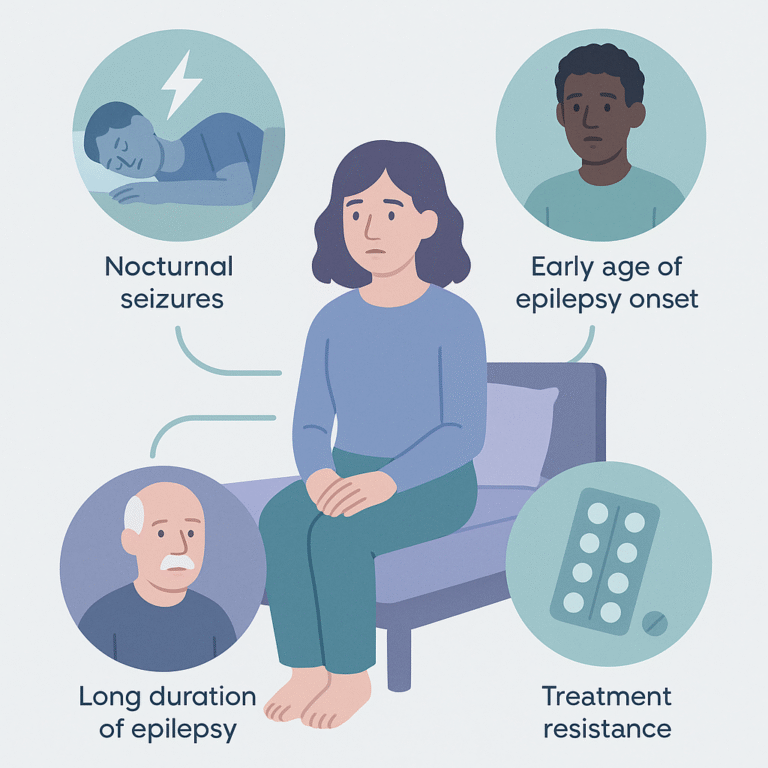
This study looked at sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP), which is a major cause of death related to epilepsy.
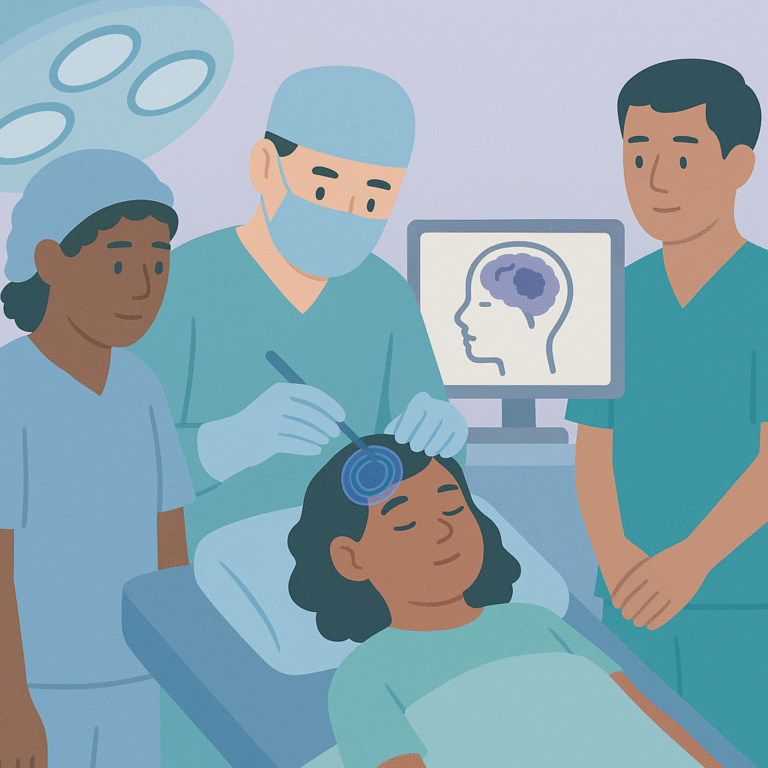
Researchers studied children with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) to find better ways to predict the success of epilepsy surgery.
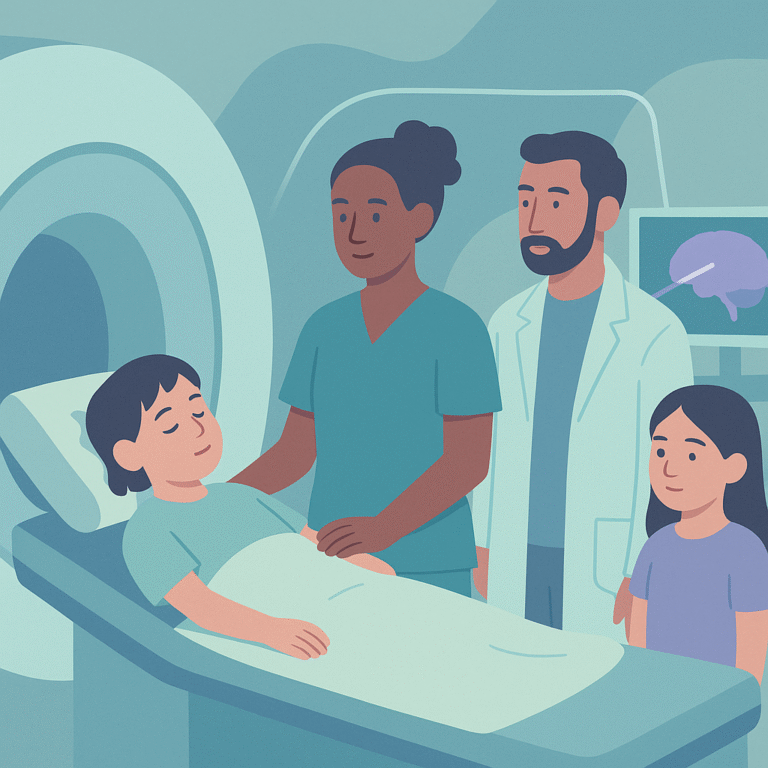
Researchers studied the use of magnetic resonance-guided laser interstitial thermal therapy (MRgLITT) as a treatment for children with drug-resistant epilepsy, which means their seizures do not respond to standard medications.
Researchers studied how much of a brain tumor called glioma should be removed during surgery.